|
1234 Washington Street
|
|
|
|
1234 Washington Street
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Step 1: Determining Your Total LoadIn order to design your system the first thing that must be done is to determine the load that you will be lifting. This load (expressed in pounds) will be referred to as P. This load should be the maximum weight of any and all objects you intend to lift with this system, including any slings, spreader bars, grabs, load tables, or other devices used to help lift the objects off the ground. Step 2: Determining Your Length Of LiftNext you will need to find the length of the lift that will be required. The way to do this is the measure from the bottom of where the monorail is to be mounted, down to the floor. Or down to the bottom of the pit, if this system is to lift its load out of a pit or opening in the floor. From this dimension you can subtract the height of the object that you are going to be lifting. This will leave you with the maximum life length you will need, this will be referred to as L.
Step 3: Selecting The Appropriate HoistThe next thing to do is to select the correct hoist for your application. Determining the correct hoist will depend on a number of factors, these include: the weight of your load (P), the length of the lift required (L), the speed(s) required of the hoist, whether a chain or wire rope is desired, and the method used to power the hoist (manual, electric, hydraulic, air).   
Step 4: Selecting The Correct Trolley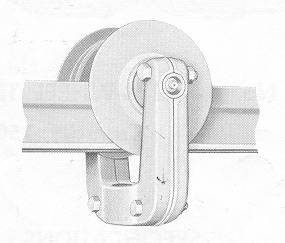
What type of trolley you will need for your system? There are three main types of trolleys to chose from, a standard push trolley, and hand geared trolley (uses a gear and chain to move the trolley), and a motorized trolley. There are obviously benefits to each, but the choice is really based on your application. 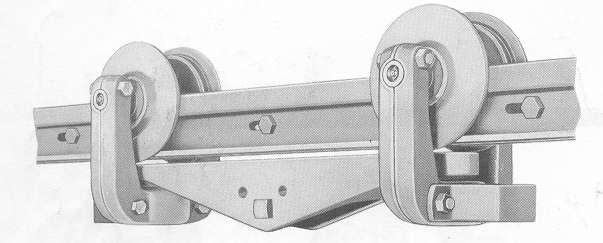
One important thing to remember is that you can not have a motorized trolley if you are planning on having any switches in your system. If switches are required and you still want motorized movement you will have to use a tractor to pull the trolley, see step 9. Step 5: Determining Hanger Spacing And Track SelectionNext you need to determine how often you can place hangers for the monorail track. This will depend on how the building you are installing this system in is designed. The more frequently you can place the hangers, the greater the load you can support on a smaller and less expensive track. Here are links to the load charts for the various rail choices we offer, they go in order form lightest rail to heaviest to help you find the best option for you. Hanger Spacing TablesStep 6: Calculating Hanger Rod LengthsIn order to calculate the length of your hanger rods there is only one piece of information you need to have, that is the height of any overhead obstructions that are going to be in the way of the monorail that must be accounted for in the design. Once you know this you know how far down the track needs to be dropped, and this is your hanger rod length. 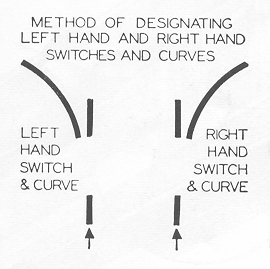 Step 7: Designing Track Layout
Step 7: Designing Track Layout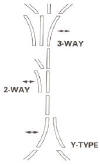
This
step is centered around what you need for your facility. Based on how
your facility is laid out, and how you intend to use the system you must
decided where the hoist must be able to travel in order to service your
needs.
Any place that you need to have the trolley turn from one section of track on to another section you will need a switch, the switch must be placed 4 feet before the section of track you are turning onto in order to complete the switch. Also when planning any curves or turns in the track, plan on starting the curve 4 feet before you want to finish it.
Step 8: Electrification (optional)If you have either a motorized trolley or hoist or both, you need to also have a method of electrification in order to supply power to these items. There are two main options when it comes to electrification, there is a KANT-SHOCK conductor bar system, or a Festoon system. The advantage to the Festoon system is that it eliminates mobile collectors which will prevent sparks, small electrical arcs, and loss of energy. Festoons however are not good for systems where there will be multiple trolleys or if the extra storage space that is required by the festooning trolleys (about 5% of the total length of the system) is not available. The advantages of the conductor bar system is that it can handle multiple trolley/hoist setups at the same time, can handle a higher ampacity allowing for larger and more power drawing items, and it requires no extra length. Both systems can been seen at this page Conductors Step 9: Selecting A Monotractor (optional)If your system requires motorized trolley movement, but also requires that you have track switches, then a monotractor is you solution. A monotractor will run in front of your hoist and trolley, and will be connected to that trolley by a load bar. The monotractor uses a rubber drive wheel to pull itself, and your load along the track, its special design allows it to negotiate the tight curves of monorail curves and switches.
|